apiserver.yaml
The configuration file supports environment variable injection using the ${VAR:default} syntax. If the environment variable is not set, the default value will be used.
Common practice is to inject values through different .env, .env.development, .env.prod files, or you can directly modify the configuration with hardcoded values.
Chat Message Database Configuration
This configuration is specifically for storing chat messages in the backend (though it can share the same database with proxy configurations). It corresponds to the information shown in the image below:
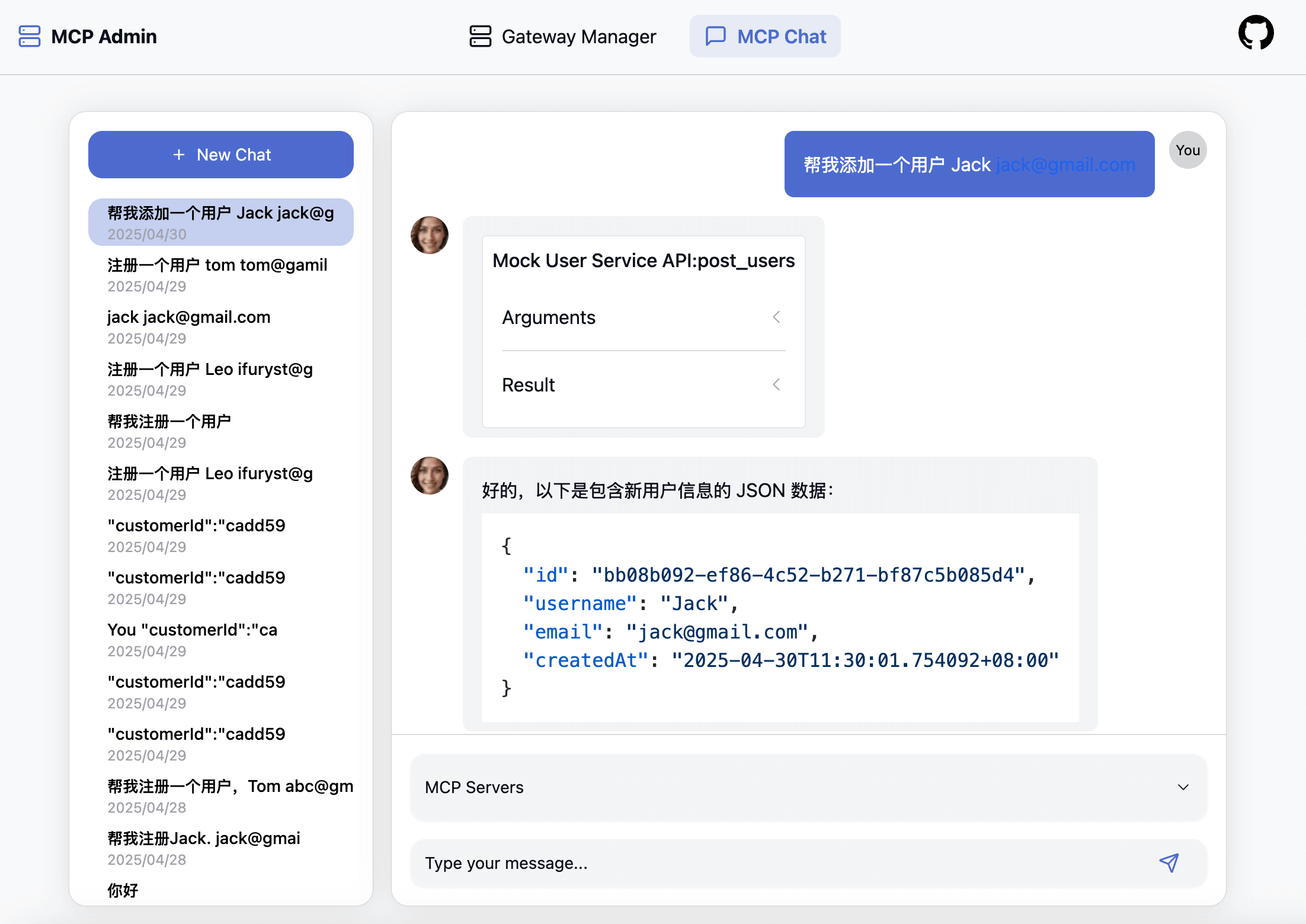
Currently supports 3 types of databases:
- SQLite3
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
If you need to add support for additional databases, you can request it in the Issue section, or you can implement the corresponding implementation and submit a PR :)
database:
type: "${APISERVER_DB_TYPE:sqlite}" # Database type (sqlite, postgres, mysql)
host: "${APISERVER_DB_HOST:localhost}" # Database host address
port: ${APISERVER_DB_PORT:5432} # Database port
user: "${APISERVER_DB_USER:postgres}" # Database username
password: "${APISERVER_DB_PASSWORD:example}" # Database password
dbname: "${APISERVER_DB_NAME:./mcp-gateway.db}" # Database name or file path
sslmode: "${APISERVER_DB_SSL_MODE:disable}" # SSL mode for database connection
Gateway Proxy Storage Configuration
This is used to store gateway proxy configurations, specifically the mappings from MCP to API, as shown in the image below:
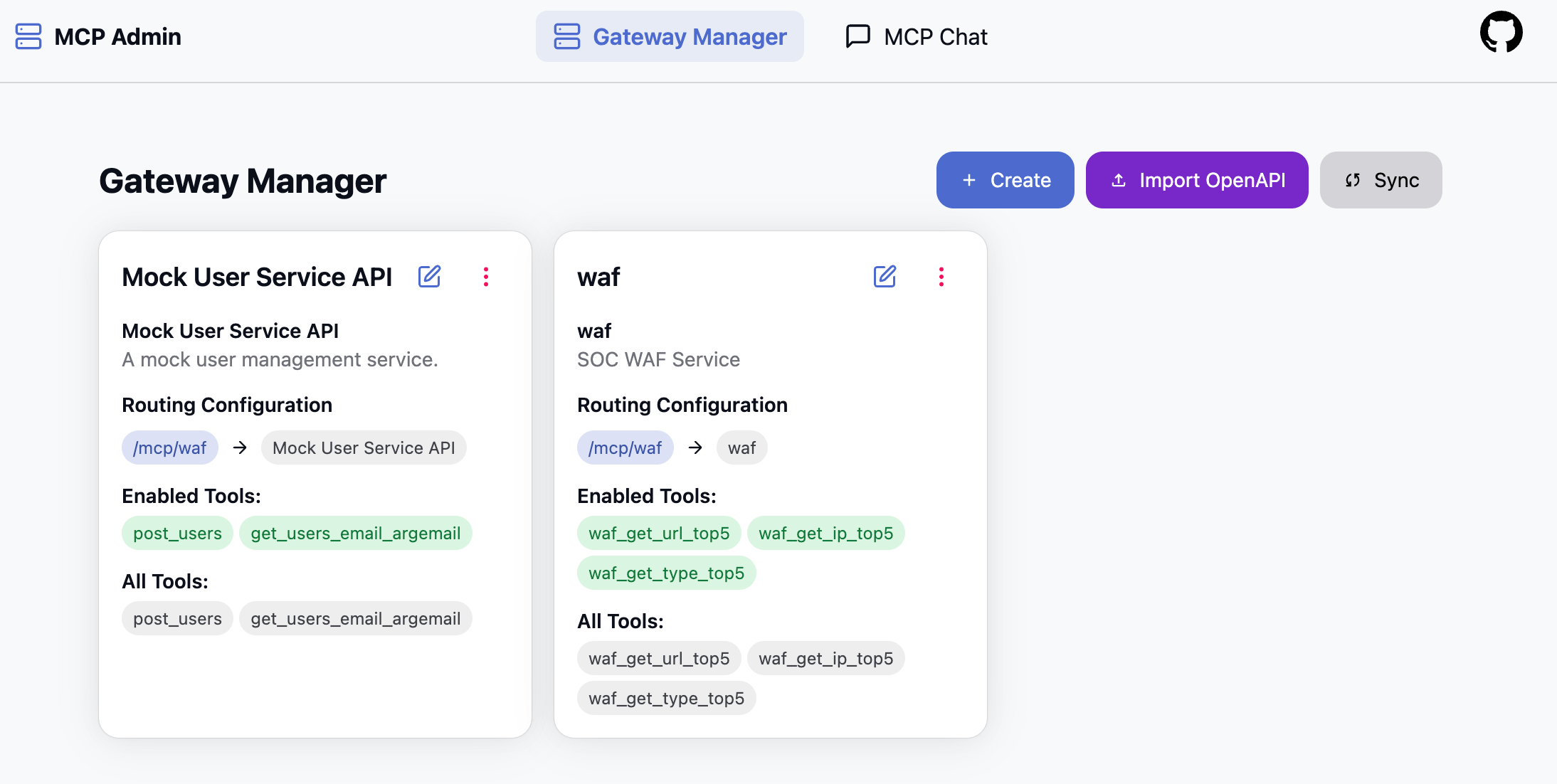
Currently supports 2 types:
- disk: Configurations are stored as files on disk, with each configuration in a separate file, similar to nginx's vhost concept, e.g.,
svc-a.yaml,svc-b.yaml - db: Store in database, each configuration is a record. Currently supports three types of databases:
- SQLite3
- PostgreSQL
- MySQL
storage:
type: "${GATEWAY_STORAGE_TYPE:db}" # Storage type: db, disk
# Database configuration (used when type is 'db')
database:
type: "${GATEWAY_DB_TYPE:sqlite}" # Database type (sqlite, postgres, mysql)
host: "${GATEWAY_DB_HOST:localhost}" # Database host address
port: ${GATEWAY_DB_PORT:5432} # Database port
user: "${GATEWAY_DB_USER:postgres}" # Database username
password: "${GATEWAY_DB_PASSWORD:example}" # Database password
dbname: "${GATEWAY_DB_NAME:./data/mcp-gateway.db}" # Database name or file path
sslmode: "${GATEWAY_DB_SSL_MODE:disable}" # SSL mode for database connection
# Disk configuration (used when type is 'disk')
disk:
path: "${GATEWAY_STORAGE_DISK_PATH:}" # Data file storage path
Notification Configuration
The notification module is primarily used to notify mcp-gateway of configuration updates and trigger hot reloads without requiring service restart.
Currently supports 4 notification methods:
- signal: Notify through operating system signals, similar to
kill -SIGHUP <pid>ornginx -s reload. Can be triggered via themcp-gateway reloadcommand, suitable for single-machine deployment - api: Notify through an API call.
mcp-gatewaylistens on a separate port and performs hot reload when receiving requests. Can be triggered viacurl http://localhost:5235/_reload, suitable for both single-machine and cluster deployments - redis: Notify through Redis pub/sub functionality, suitable for both single-machine and cluster deployments
- composite: Combined notification, using multiple methods. By default,
signalandapiare always enabled, and can be combined with other methods. Suitable for both single-machine and cluster deployments, and is the recommended default approach
Notification roles:
- sender: Sender role, responsible for sending notifications.
apiservercan only use this mode - receiver: Receiver role, responsible for receiving notifications. Single-machine
mcp-gatewayis recommended to use only this mode - both: Both sender and receiver roles. Cluster-deployed
mcp-gatewaycan use this mode
notifier:
role: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_ROLE:sender}" # Role: sender, receiver, or both
type: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_TYPE:signal}" # Type: signal, api, redis, or composite
# Signal configuration (used when type is 'signal')
signal:
signal: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_SIGNAL:SIGHUP}" # Signal to send
pid: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_SIGNAL_PID:/var/run/mcp-gateway.pid}" # PID file path
# API configuration (used when type is 'api')
api:
port: ${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_API_PORT:5235} # API port
target_url: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_API_TARGET_URL:http://localhost:5235/_reload}" # Reload endpoint
# Redis configuration (used when type is 'redis')
redis:
addr: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_REDIS_ADDR:localhost:6379}" # Redis address
password: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_REDIS_PASSWORD:UseStrongPasswordIsAGoodPractice}" # Redis password
db: ${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_REDIS_DB:0} # Redis database number
topic: "${APISERVER_NOTIFIER_REDIS_TOPIC:mcp-gateway:reload}" # Redis pub/sub topic
OpenAI API Configuration
The OpenAI configuration block defines settings for OpenAI API integration:
openai:
api_key: "${OPENAI_API_KEY}" # OpenAI API key (required)
model: "${OPENAI_MODEL:gpt-4.1}" # Model to use
base_url: "${OPENAI_BASE_URL:https://api.openai.com/v1/}" # API base URL
Currently only integrates OpenAI API-compatible LLMs calls